What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?: A Complete Guide
Robotic accounting involves the use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to streamline and automate accounting tasks like data entry, reconciliation, report generation, and financial analysis. This article covers how RPA in accounting works, its applications, benefits, and how to overcome its limitations with intelligent automation tools.
Accounting has always been a field that values precision and accuracy, and with the advent of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), achieving these standards has become significantly easier.
Commonly referred to as robotic accounting, RPA in accounting is changing the landscape of the profession, allowing for more efficiency, consistency, and accuracy in accounting tasks.
In essence, robotic accounting is the application of RPA technology to automate the repetitive, rule-based tasks that are prevalent in accounting. This technology uses software robots or 'bots' to replicate the actions of a human user, thereby automating many manual processes.
In this practical guide, we will delve into the relevance of robotic accounting, its benefits, and the best strategies for implementing robotics in accounting.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, is a form of business process automation technology that uses software robots or 'bots' to perform routine tasks traditionally done by humans. These bots can be programmed to follow rules-based procedures, and they interact with digital systems in the same way a human user would.
The key features of RPA include:
- Perform tasks based on predefined rules and instructions.
- Ability to interact with any software or system, just as a human would.
- Seamless integration without requiring changes to existing systems or infrastructure.
- High speed and accuracy in executing tasks, reducing errors and increasing productivity.
How does robotic accounting work?
Robotic process automation (RPA) accounting employs programmable software bots to automate repetitive financial tasks efficiently. Unlike a Microsoft Excel macro limited to one system, robotic process automation in accounting operates with enhanced power and reach, streamlining processes across multiple systems for increased efficiency and accuracy.
If you have ever written scripts in Excel to automate certain repetitive tasks, then you've already got a taste of what robotic accounting can do, but on a much smaller scale.
In robotic accounting, software robots or 'bots' are programmed to perform tasks traditionally done by accountants. These can include anything from data entry and accounts payable management to performing audit tests and generating financial reports.
Like your scripts, these bots follow predefined rules and procedures, but unlike them, RPA tools can interact with multiple software systems and complete complex tasks in a fraction of the time.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how robotic accounting works:
Identify tasks for automation: The first step is identifying the tasks that are suitable for automation. These are typically high-volume, rule-based tasks that don't require complex decision-making.
Configure the bots: Once the tasks have been identified, the next step is to configure the software bots. This involves programming them with the rules and instructions to perform the tasks.
Run the bots: The configured bots are then run on the accounting software or systems. They perform the tasks just as a human would, interacting with the software, entering data, and generating reports.
Monitor and maintain the bots: The final step is monitoring the bots to ensure they're performing their tasks accurately. This can involve regular checks and updates to the bots as required.
Examples of how robotic accounting can be used in accounting processes
According to a Deloitte survey, more than 90% of organizations believe that RPA has met or exceeded their expectations in terms of productivity improvement, compliance improvement, and cost to implement.
It goes without saying that the potential of robotic accounting is vast, and its applications can significantly transform the accounting sector.
Here are a few examples of how RPA can be applied in accounting:
Invoice processing: RPA can be used to automate the process of sorting and processing invoices. The bot can scan incoming invoices, extract the relevant data, match invoices with purchase orders, and even initiate payments. This not only speeds up the process but also eliminates the risk of human error.
Payroll processing: RPA can also be employed in payroll processing. The bot can calculate salaries based on attendance and other parameters, generate pay slips, and transfer payments to employees' bank accounts. This ensures that everyone is paid correctly and on time.
Financial reporting: Financial reporting is a time-consuming and error-prone process. But with RPA, all the data required for financial reports can be collected, organized, and presented in a streamlined manner. The bot can pull data from various sources, perform the necessary calculations, and generate reports, reducing the time taken and ensuring accuracy.
Bank reconciliation: The bot can match entries from the bank statement with the company's internal financial records, quickly identifying any discrepancies and alerting the relevant staff. This process, which could take hours if done manually, can be completed in a matter of minutes with RPA.
Audit processes: The bot can access and analyze large volumes of data from multiple sources, identify anomalies or irregularities, and create detailed audit reports. This enhances the efficiency and accuracy of the audit process, and allows auditors to focus on higher-level tasks that require professional judgment.
Benefits of Robotic Accounting
Aren’t we all a little tired of tedious, repetitive tasks that consume valuable time? Think of all the spreadsheets you've had to manually update, the invoices you've had to painstakingly process, and the countless reports you've had to generate.
Robotic accounting can take over these repetitive tasks, freeing up your time to focus on more strategic tasks - a definitive accounting best practice that should be considered. Here are some of the key advantages of using robotic accounting:
1. Cost efficiency
Accounting automation through RPA can significantly reduce the labor costs associated with these tasks. For instance, a bot can handle the process of invoice processing or payroll calculation, allowing your staff to focus on more strategic or complex tasks.
This not only reduces the need for additional hires but also decreases the likelihood of costly errors that can occur with manual processing.
2. Increased accuracy
Repetitive tasks are mind-numbing. When performed manually, they are prone to human errors. Bots, on the other hand, are highly accurate. Once programmed with the correct rules and procedures, they can execute tasks without errors, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
For example, a bot performing bank reconciliation will not miss any discrepancies between the bank statement and the company's records, ensuring financial accuracy.
3. Enhanced productivity
Your staff would no longer be bogged down by mundane and repetitive tasks, which means they can focus on more significant, value-adding tasks. This can lead to an increase in productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
For instance, while the bot takes care of the financial reporting, your team can analyze the reports and devise strategic financial plans.
4. Improved compliance
Bots can be programmed to log in to different systems and update and maintain records as and when required. This ensures all records and transactions are up-to-date and compliant with the necessary regulations.
For instance, a bot can be designed to create purchase orders every time a request for goods or services is approved.
5. Enhanced data security
Bots can be programmed to adhere strictly to internal access controls, reducing the risk of data breaches. For instance, when processing payroll, the bot can securely handle employees' sensitive information and ensure it's not exposed to unauthorized access.
6. Scalability
Bots can easily scale up or down to meet this demand, without any compromise on speed or accuracy. This flexibility means that you can handle growth or sudden spikes in demand without needing to recruit more staff or invest in additional resources.
7. Round-the-clock operation
Bots can work 24/7 without breaks. This means that tasks can be performed outside of traditional working hours, ensuring smooth operations and faster turnaround times.
For instance, a bot can process invoices or reconcile bank transactions during off-peak hours, reducing the workload during the day and speeding up the overall process.
The challenges of implementing robotic accounting
Think about the time your vacuum cleaner got stuck on a rug — it's a simple reminder that not all tasks can be fully automated without human intervention.
Similarly, introducing robotic accounting into your business operations will also have its own set of challenges.
Here are the main challenges that businesses might face when implementing robotic accounting:
1. Technical glitches
Just like any other technology, RPA can have technical glitches that can disrupt the automation flow. Let’s say the Google Workspace account connected to your RPA bot gets logged out, the bot will not be able to perform its tasks unless it gets logged back in. This requires human intervention and monitoring to ensure the bot operates smoothly.
2. Complexity of tasks
While RPA is great at handling repetitive and rule-based tasks, it might struggle with complex tasks that require judgment or decision-making. For instance, while a bot can collect your invoice data and process it, it might not be able to recognize when an invoice contains unusual charges or discrepancies that require further investigation.
3. Dependency on existing systems
RPA bots rely heavily on existing software and systems to perform their tasks. If these systems are updated or go through any major changes, the bots might not be able to perform their tasks efficiently without being reprogrammed or updated. This can lead to inefficiencies and potential downtime.
4. Data privacy and security concerns
While bots can be programmed to adhere to data security protocols, there are still potential risks. If a bot is hacked, it could expose sensitive data and potentially lead to a data breach.
Moreover, if a bot is not programmed correctly, it might accidentally violate data privacy laws.
5. Lack of human touch
Although robots can perform many tasks more efficiently than humans, there are still some tasks that require the human touch. For instance, customer service interactions or decision-making needs empathy and understanding of nuanced contexts, which robots might not be equipped to handle.
5. Lack of buy-in from staff
If the employees are not trained properly, they may resist the change and not fully utilize the bots, leading to underutilization of the technology. There may also be fear or apprehension about job security, leading to resistance.
Therefore, it's essential to communicate the benefits of RPA clearly to the staff and provide adequate training and support to ensure smooth adoption.
6. Inadequate integrations
While RPA bots can be programmed to work with various systems, they might not seamlessly integrate with all types of software or platforms. If such incompatibilities exist, it could lead to inefficiencies and require additional manual intervention.
For instance, if a bot is designed to pull data from a specific accounting software, but the software is replaced with a different one, the bot will need to be reprogrammed to work with the new platform.
The impact of robotic accounting on the accounting profession
The global RPA market size is expected to increase from $1.40 billion in 2019 to $11 billion in 2027 according to Grand View Research. This indicates a growing acceptance of RPA and robotic accounting in modern workplaces.
However, it's essential to understand that the increase in automation doesn't necessarily mean a decrease in the need for human accountants. Instead, it changes the nature of their roles and responsibilities by:
Shift in roles: With the implementation of robotic accounting, the role of accountants is shifting from manual data entry and report generation to more strategic roles. They are now required to interpret and analyze the data provided by the bots and make informed business decisions based on these insights.
Increased demand for tech-savvy accountants: As businesses increasingly adopt automation, there is a growing need for accountants who are comfortable working with technology. These accountants need to understand how to use RPA tools effectively, how to troubleshoot issues, and how to adapt to the changing technological landscape.
Emphasis on strategic decision-making: The integration of RPA in the accounting process places a greater emphasis on strategic decision-making. Accountants are now less burdened by mundane tasks and can focus more on providing strategic insights and advice. They are expected to interpret the data generated by the bots and use this to guide business strategy and decisions.
Higher efficiency and accuracy: The use of RPA in accounting increases the efficiency and accuracy of financial processes. By automating repetitive tasks, accountants can focus more on tasks that require human intelligence and expertise, leading to more accurate outcomes and improved productivity.
Greater compliance and control: With bots handling the data, there is a reduced risk of human error and increased adherence to compliance regulations. Moreover, the use of RPA can provide greater control over financial processes as bots can be programmed to follow specific rules and protocols. This also ensures consistency in the processes and helps in maintaining audit trails.
Risk management: RPA also aids in risk management by providing real-time data and insights. This allows accountants to identify potential issues and risks promptly, enabling proactive management.
How can intelligent automation make up for the limitations of robotic accounting?
Intelligent automation combines RPA with artificial intelligence (AI), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and machine learning (ML) to overcome some of the limitations of robotic accounting.
Nanonets can be used to digitize documents and extract relevant data, which can then be processed by AI and ML algorithms for intelligent decision-making. This helps in automating complex accounting tasks that require an understanding of context and rules.
For instance, Nanonets’ intelligent automation can help automate the entire invoice processing workflow, from receipt to payment. It can extract data from invoices, validate it against purchase orders, identify discrepancies, and even make payment decisions based on predefined rules.
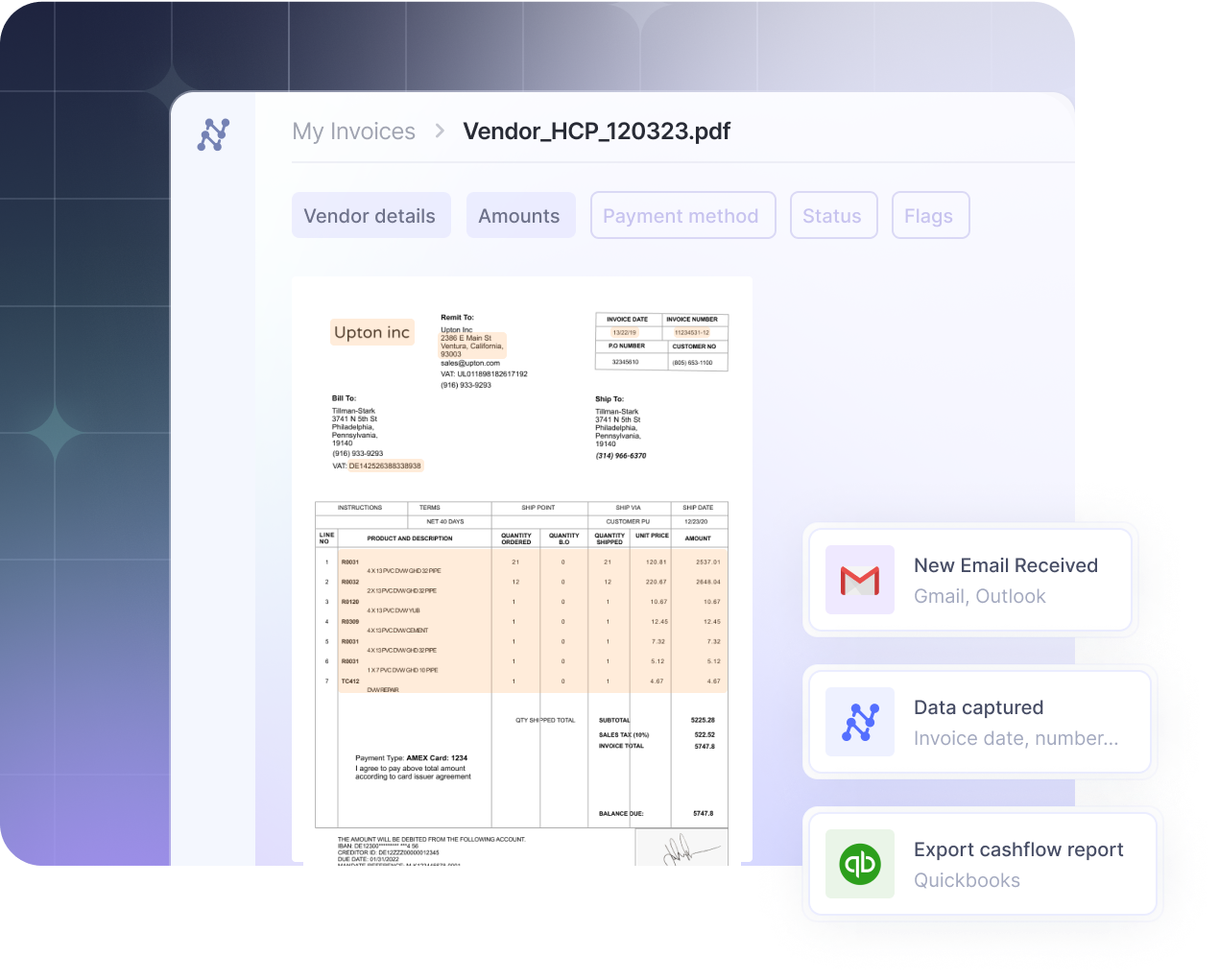
This significantly reduces manual intervention, eliminates errors, and accelerates the entire process. Moreover, the AI/ML component enables the system to learn and improve over time, handling exceptions and unusual cases more efficiently.
Final thoughts
While robotic accounting has its limitations, the combination of RPA with AI, OCR, and ML offers promising solutions. It can automate complex tasks while improving accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, it allows accountants to focus more on strategic roles, increasing their value within organizations.
Nanonets is an excellent tool for businesses looking to adopt intelligent automation. With its advanced features and easy-to-use interface, it can significantly streamline the accounting process and improve productivity.
Adopting such technology not only offers immediate benefits but also prepares businesses for future advancements. As AI and ML continue to evolve, they will offer even more sophisticated solutions to automate and improve business operations.
Want to find out more about how Nanonets can transform your accounting processes? Reach out to our team for a demo and understand how we can address your unique business needs.
FAQs
How does robotics affect accounting?
Robotics, particularly in the form of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), significantly impacts accounting by automating repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and accuracy, and reducing the risk of human error. This shift allows accountants to focus on more strategic roles, like interpreting data and making informed business decisions.
What is an example of robotic process automation in accounting?
An example of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in accounting is invoice processing automation. Tools like Nanonets can extract data from invoices, validate it against purchase orders, identify discrepancies, and make payment decisions based on predefined rules. This reduces manual intervention and accelerates the entire process.
How is robotics used in finance?
In finance, robotics automates repetitive and manual tasks, providing real-time data and insights for risk management and improving compliance and control over financial processes. For instance, RPA can be used for financial tasks like transaction processing, audit reporting, and fraud detection.
Can robots take over accounting?
While robots can automate many accounting tasks, they cannot fully take over the role of human accountants. Tasks requiring human judgment, interpretation, strategic decision-making, and understanding complex rules and contexts still need human accountants. However, integrating AI and machine learning can help address some of these limitations.
How is robotics used in accounting?
Accounting uses robotics to automate routine tasks such as data entry, transaction processing, and invoice management. By leveraging tools like Nanonets, businesses can automate complex workflows and significantly reduce manual intervention, increasing accuracy and efficiency.
How does robotic process automation affect accounting?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) affects accounting by taking over repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of human error, and increasing efficiency. It also ensures greater compliance and control by following specific rules, aiding in risk management by providing real-time data and allowing for proactive management.
What is robotic process automation in audit and accounting?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software bots to automate repetitive and manual tasks such as data entry, transaction processing, and audit reporting in audit and accounting. These bots follow predefined rules, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. RPA can also provide real-time data for risk management and aid in ensuring compliance.
What are the advantages of robotic process automation in accounting?
The advantages of RPA in accounting include increased efficiency and accuracy, reduction in human error, real-time data for risk management, and improved compliance and control. Additionally, it frees up accountants to focus on more strategic tasks, adding more value to the organization. It also prepares businesses for future advancements in AI and machine learning.





.png)

.png)

.png)

.png)















