Vendor invoice management: How to efficiently process them?
Vendor invoices are important. You already know that. But when companies spend an average of $15 to $40 to process a single invoice, it's clear that managing these invoices is just as crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the ins and outs of vendor invoice management, detailing how to improve efficiency and accuracy in your business.
What is a vendor invoice?
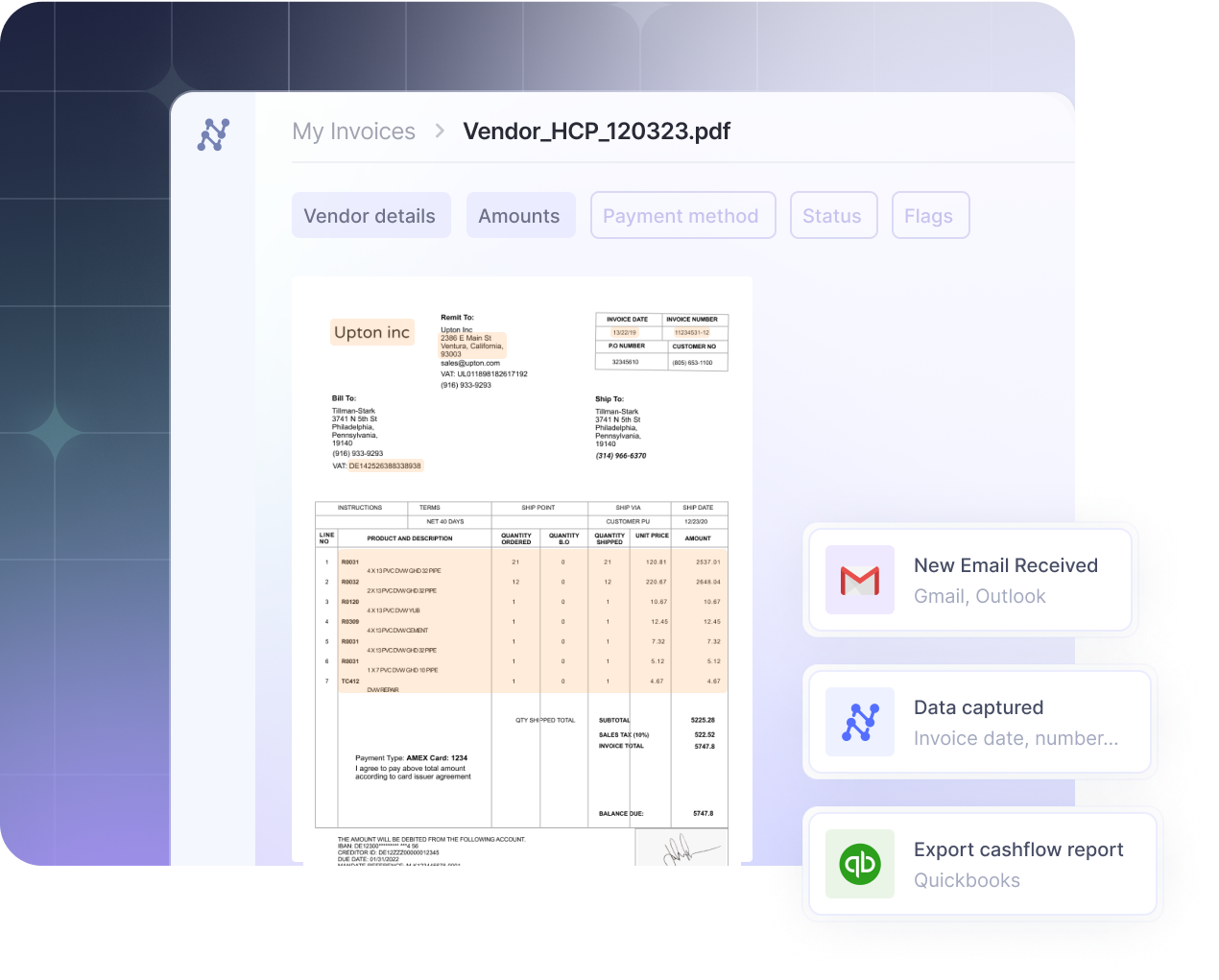
A Vendor Invoice is a formal request for payment from a supplier or vendor detailing goods or services provided, their quantities, and their respective costs. These invoices are a critical link in the supply chain, facilitating transactions between businesses and their vendors.
Vendor invoice processing encompasses the entire cycle of handling supplier invoices within an organization. It involves receiving the invoice, verifying and approving it, establishing a remittance date, making payment, and accurately recording the transaction in the general ledger. This process is essential for the smooth operation and financial integrity of a business.
Whether you're a retail store, a manufacturer, or a business-to-business (B2B) enterprise, vendor invoices are an integral part of your operations. They help you track expenses and ensure your suppliers are paid accurately and on time.
The importance of vendor invoice management
Vendor invoice management is about more than just paying your vendors. It's about streamlining your processes, reducing errors, and saving money.
With effective vendor invoice management, you can:
1. Complete the purchase cycle effectively: Vendor invoices mark the end of your purchase cycle. By managing them effectively, you can ensure that all your transactions are completed successfully and on time.
2. Improve accuracy: Approximately 40% of all invoices contain errors. Effective management can drastically reduce these errors, ensuring you only pay for what you've received.
3. Save time and money: Manual invoice processing can take up to 8.3 days and cost between $15 and $40 per invoice. Streamlining your invoice management can significantly reduce these costs and free up valuable time.
4. Enhance supplier relationships: Timely and accurate payments can help build stronger relationships with your suppliers, leading to better terms and potentially lower costs in the future.
5. Improve cash flow: Vendor invoices include payment dates, amounts, and new stock arrivals. By managing them effectively, you can clearly understand your cash flow and plan your budget accordingly. You can plan your cash flow more accurately and avoid late payments and penalties.
The components of a vendor invoice
Are all invoices created equal? Not quite. Although they serve the same purpose – to request payment for goods or services – vendor invoices can vary significantly in their components.
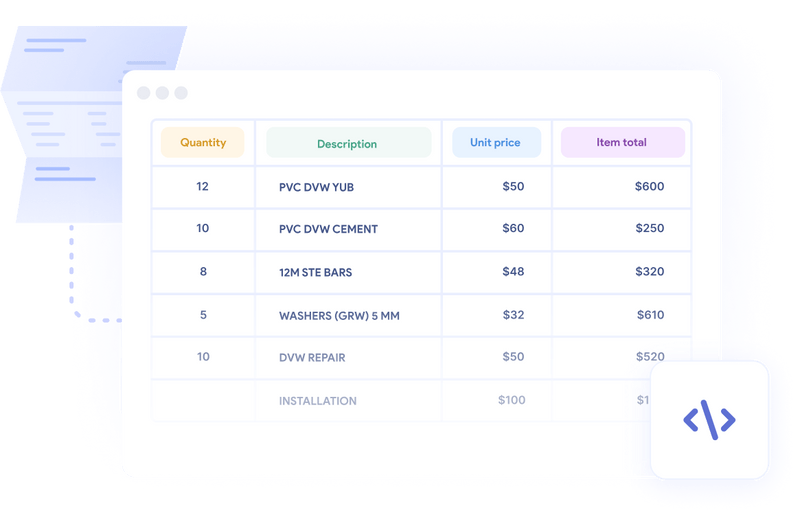
Let's break down the typical elements of a vendor invoice:
1. Vendor information: This includes the vendor's name, address, contact details, and possibly a unique identification number like a Tax Identification Number (TIN) or a Vendor Identification Number (VIN). The buyer must know who the invoice is from and where to send the payment.
2. Invoice number: The invoice number is unique to each invoice and is used for tracking and reference purposes. It's essential for organizing and managing invoices.
3. Date: The invoice date is the day the invoice is issued. This date is essential for the vendor and buyer to record-keeping and determine payment due dates.
4. Buyer's information: Similar to the vendor information, this includes the buyer's name, address, and contact details. It allows the vendor to know who the invoice is for and where to send goods or services
5. Description of goods or services: This section provides a detailed description of the goods or services provided, including the quantity, price per unit, and total cost. It gives the buyer and the vendor a clear understanding of what the invoice covers.
6. Terms of payment: This outlines the payment agreement between the buyer and the vendor. It can include information like payment due dates, discounts for early payment, payment modes, and penalties for late payment.
7. Subtotal: This is the total cost of all the goods or services before any taxes or discounts are applied.
8. Taxes and discounts: If applicable, taxes and any discounts are listed separately and then added or subtracted from the subtotal to give the final total.
9. Total amount due: This is the final amount that the buyer owes the vendor after all taxes and discounts have been applied.
Minimizing errors in these components is essential for accurate record-keeping and financial management.
Types of invoices
Some invoices are straightforward, detailing a simple transaction between the vendor and the buyer. However, there are different types of invoices, each serving a unique purpose.
Understanding these different invoice types can help you manage them more effectively.
1. Purchase order-based invoices: These are linked to a specific purchase order issued by the buyer. The purchase order number is included on the invoice, making it easier to match the order with the invoice. This type of invoice is often used in industries where large, complex orders are common.
2. Recurring invoices: These are used for ongoing services or products provided regularly. The invoice details are usually the same for each period except for the date.
3. Credit invoices: Also known as credit memos, these are issued when there is a need to decrease the amount that the buyer owes. This could be due to returns, discounts, or errors in the original invoice.
4. Debit invoices: The opposite of credit invoices, these increase the amount that the buyer owes. They are used when additional charges or adjustments should have been included in the original invoice.
- Pro forma invoices: These are preliminary invoices sent before the delivery of goods or services. They provide an estimate of the cost and are not a demand for payment.
6. Timesheet invoices: These are used when billing for hours worked, often by freelancers or contractors. They detail the number of hours worked, the rate per hour, and the total amount due.
7. Progress billing invoices: These invoices are commonly used in long-term projects and are issued at various stages of the project. They provide details about the work completed during a particular phase and the corresponding cost. This type of invoice helps to ensure a steady cash flow throughout the duration of the project.
8. Commercial invoices: These are used in international trade and contain details about the goods being shipped, their value, and the parties involved. They are used for customs declaration and assessment of duties and taxes.
9. Non-purchase order: These invoices are not linked to a specific purchase order. They are typically used for ad hoc purchases or services that don't require a purchase order. Employee expenses, utility bills, and professional services are examples of costs often covered by non-purchase order invoices.
10. Consolidated invoices: These are a summary of multiple invoices, typically sent monthly to the buyer. They simplify the payment process by combining several invoices into one, making it easier for the buyer to manage their payments.
More vendor invoices may be specific to certain industries or transactions, but these are the most common ones you'll encounter in most businesses.
How does the vendor invoice management process work?
The vendor invoice management process involves several steps designed to verify, approve, and pay vendor invoices promptly and efficiently. It also helps to maintain accurate financial records, which are crucial for any business.
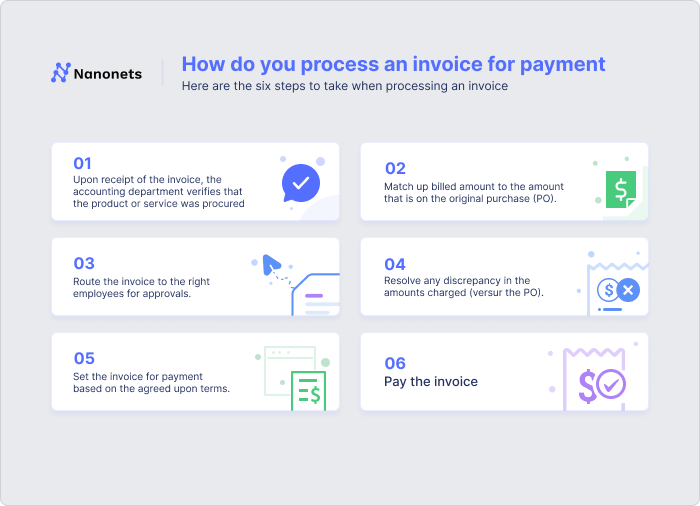
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of a typical vendor invoice management process:
1. Purchase order creation: A document is sent by the buyer to the vendor detailing the goods or services required, the price, delivery date, and other terms and conditions. This document serves as a legal offer to buy.
2. Receipt of goods or services: The procurement team of the buyer receives the goods or services from the vendor per the details mentioned in the purchase order.
3. Receipt of invoice: The vendor sends an invoice to the buyer after the goods or services have been delivered. This invoice should match the details on the purchase order.
4. Invoice verification: The buyer validates the invoice details against the purchase order and the goods or services received to ensure everything matches. Any discrepancies are flagged and reported to the vendor for correction.
5. Invoice approval: Invoices typically undergo multiple levels of approval within the buyer's organization. This helps to ensure the accuracy of the invoice and that all goods or services have been received as expected. Once approved, the invoice is ready for payment.
6. Payment processing: The payment is made using the agreed-upon method, such as direct deposit, check, or online transfer. Processing the payment within the agreed-upon terms is essential to avoid late payment penalties.
7. Record keeping: All invoices and payments are recorded and filed for future reference and auditing purposes. This step is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and helps in budgeting, financial planning, and tax filing.
8. Audit and review: The invoices and payments are regularly audited to ensure accuracy and compliance with the company's policies and procedures. This also includes a review of the vendor invoice management process itself to identify any areas of improvement. For instance, if there are recurring discrepancies in a specific type of invoice, the process for verifying that invoice might need to be revised.
This is how the vendor processing cycle works in a typical organization. Remember, each business might slightly vary this process due to their specific needs and requirements.
It may seem complex, but managing vendor invoices can be straightforward and efficient with suitable systems and workflows.
Let’s look at how businesses can manage or optimize these steps in the vendor invoice management process.
1. Optimizing purchase order creation
Utilize a purchase order system that automates the creation of a purchase requisition. This not only reduces manual errors but also speeds up the process.
Employees won’t have to fill out paper forms manually; the system can instantly send the PO to the vendor, saving time. You can set up predefined approval workflows in the system to ensure that the PO is reviewed and approved by the right people before it's sent out.
2. Improving receipt of goods or services
Implement a receiving process that includes checking the goods or services against the purchase order upon delivery. This can help catch any discrepancies early and avoid potential disputes with the vendor later on.
For instance, if a shipment arrives with fewer items than ordered, the receiving team can immediately report the discrepancy and request a correction or adjustment from the vendor. This proactive approach helps minimize discrepancies and reduces the time spent on invoice verification later on.
3. Streamlining invoice approval
An automated approval workflow routes invoices to the appropriate individuals or departments for approval. This ensures that invoices are reviewed and approved promptly.
For example, a system could be set up so that invoices below a certain amount are automatically approved, while those above a certain threshold require multiple levels of approval. This speeds up the approval process, adds an extra layer of AP control, and helps prevent fraud or overspending.
4. Enhancing payment processing
Implement a digital payment system that allows for quicker, more efficient processing of payments. This could include direct deposit, online transfers, or even digital wallets.
Setting up automated reminders for due payments is also beneficial to avoid late payment penalties. This system can be configured to notify the accounts payable team before the due date, ensuring payments are made on time.
5. Maintaining accurate records
Invest in a robust document management system to help you track all invoices and payments. This system should allow for easy retrieval of documents when needed, such as during audits or financial reviews.
To further enhance record keeping, consider digitizing all documents. Digital documents are easier to store, retrieve, and manage compared to physical documents. Plus, they're less prone to damage or loss, making them a more secure option for storing critical financial records.
6. Ensuring regular audits and reviews
Schedule regular audits and reviews of your vendor invoice management process. This helps identify any potential issues or discrepancies early on, allowing for prompt correction and improvement.

This could involve engaging an internal audit team or hiring an external auditor, depending on the size and needs of your organization.
During these audits, look not just at the invoices and payments, but also at the processes and systems in place. If there are recurring issues with a particular process or invoice type, it could be a sign that the process needs to be revised or enhanced.
The best practices for vendor invoice management
Finding great vendors is just the beginning. But it is what happens next that determines the effectiveness and efficiency of your business operations.
You must constantly evaluate and optimize your vendor invoice management processes to achieve the best results.
Here are some vendor invoice management best practices to consider:
1. Automate wherever possible
Automation can drastically reduce the time spent on manual data entry and approval workflows. It can also minimize errors and ensure consistency in the process. Consider investing in software that offers features like automated invoice processing, capture, data extraction, matching, and approval workflows.
Action step: Identify the tasks in your vendor invoice management process that are repetitive and time-consuming—for example, manual data entry, invoice matching, and approval workflows. Look for software or tools that can automate these tasks.
2. Establish a clear approval process
Create an approval matrix that outlines who can approve invoices of different amounts or types. This matrix should be easily accessible to all relevant personnel. Clear communication about who is responsible for what helps avoid confusion and delays in the approval process.
Quick checklist for setting up an approval matrix:
- Who can approve invoices?
- What are the dollar amount thresholds for different levels of approval?
- Who is the backup approver when the primary approver is unavailable?
- What is the process for escalating an invoice that exceeds the highest approval threshold?
- Where to track the approval status of each invoice?
3. Establish a criteria for invoice review
Have a well-defined set of criteria for reviewing invoices. This might include checking for correct vendor details, comparing invoice amounts with POs, verifying the goods or services received, and more. Having a standard review process can help identify errors or discrepancies early and prevent payment issues.
Consider these points while establishing your criteria for invoice review:
- Are the vendor details on the invoice correct?
- Does the invoice match the corresponding purchase order?
- Have the goods or services been received, and are they satisfactory?
- Are the invoice amounts, including taxes and discounts, correct?
- Are the payment terms and due dates accurate?
4. Standardize invoice processing
Develop a standard procedure for handling invoices, from receipt to payment. This should include data entry, review, approval, and payment steps. A standardized process promotes consistency, efficiency, and accuracy in invoice management. It also makes it easier to train new staff and identify where things might go wrong.
Let’s take an example of a standardized invoice processing workflow using Nanonets:
- Invoice receipt: Communicate to the vendors that all invoices must be routed to the email address ‘accounts@xyz.com’.
- Data entry: Allow Nanonets to automatically import the invoices from the designated email address and extract the relevant data.
- Review: Set predefined rules so Nanonets can automate the review process. The invoice can be flagged for manual review if any discrepancies are found.
- Approval: Define approvers on Nanonets so the system can automatically route the invoices to the correct person based on the pre-set rules.
- Payment: Once the invoice is approved, the system can automatically schedule the payment based on the invoice's due date.
- Reconciliation: Get Nanonets to automatically match the invoice with the corresponding purchase order and delivery note. This ensures that all documentation aligns and no discrepancies exist.
- Update the accounting software: Once all steps are complete, Nanonets can automatically update your accounts payable software with the payment details and invoice status. This ensures that all your financial records stay up-to-date and accurate.
5. Regularly review and update your procedures
Regularly review the process to identify areas for improvement. This could be driven by changes in legislation, technology advancements, or changes in your business needs.
Here are some points to consider during your review:
- How effective is the current process in preventing invoice errors and discrepancies?
- How efficient is the process? Are there any bottlenecks or delays?
- How well is the process being followed by all relevant personnel? Are there any gaps in training or communication?
- Are there any new software or technologies that could improve the process?
- Have there been any changes in legislation that affect your procedures?
- Do you need to adjust your procedures to suit the current needs of your business better?
6. Maintain strong vendor relationships
Regular communication can help resolve any invoice discrepancies quickly and efficiently. Moreover, it can lead to more favorable terms, like extended payment periods or discounts.
Some tips for maintaining strong vendor relationships: provide actionable points
- Communication: Keep your vendors informed about any changes in your invoice processing procedures. Also, promptly address their queries or concerns.
- Ensure transparency: The software you use should provide a portal where vendors can track the status of their invoices and payments. This transparency builds trust and reduces the number of queries and disputes.
- Respect payment terms: Pay your vendors on time. If you anticipate a delay, inform them beforehand and explain clearly.
- Provide feedback: If there are recurring issues with a vendor's invoices, provide them with constructive feedback to help them improve. Also, be open to receiving feedback from them.
- Negotiate mutually beneficial terms: If you have a good relationship with your vendor, you might be able to negotiate more favorable payment terms, such as extended due dates or early payment discounts.
- Show appreciation: This could be a thank you note, a positive review on Google, or a referral. Small gestures can go a long way in building strong and lasting relationships with your vendors.
7. Utilize analytics and reporting
Reports generated from your invoice processing software can provide valuable data. Analyzing this data will help you identify trends, spot potential issues, and make data-driven decisions to improve your process.
Here are some points to consider:
- What is the average time taken to process each invoice? Is there scope for improvement?
- How many invoices are processed within a specific period? Is the workload manageable with the current resources, or do you need to scale up?
- How many discrepancies are identified, and how quickly are they resolved? Are there any recurring issues that need to be addressed?
- What is the average cost of processing each invoice? Can this be reduced by automating specific tasks?
- What percentage of invoices are paid on time? Are there any issues that are causing payment delays?
- Are there any patterns in the types of errors or discrepancies that occur? This could indicate a need for better training or process refinement.
- Are any specific vendors, items, or departments generating more invoice discrepancies? This could indicate a need for targeted improvements.
8. Implement a three-way matching system
A three-way match involves comparing the purchase order, the received goods or services, and the vendor invoice before payment is approved. This helps detect discrepancies or errors such as overbilling or duplicate billing.
Nanonets can streamline this process by automatically comparing these documents and flagging any mismatches for review. This reduces the risk of errors and significantly speeds up the approval process.
How Nanonets automates vendor invoice management
Imagine managing all your vendor invoices without the hassle of manual data entry, frequent errors, and time-consuming reviews. That's what Nanonets brings to the table.
Our AI-powered accounts payable software can scan and extract data from invoices, regardless of their format or language, with high accuracy. It can then automatically match this data with corresponding purchase orders and delivery notes, flag any discrepancies, route the invoice for approval, and schedule the payment. AI-powered invoice processing can update your accounting software, generate comprehensive reports, and help you analyze invoice processing performance.
Here’s how Nanonets can transform your vendor invoice management process:
Automated data extraction: Nanonets uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology to scan and capture invoice data. This reduces the need for manual data entry and decreases the chances of human error.
Three-way matching: The software automatically compares the data from the invoice, the purchase order, and the goods received note. Any discrepancies are flagged for review, streamlining the approval process.
Approval workflow: Nanonets can route invoices for approval based on your organization's hierarchy or the amount on the invoice. This ensures that invoices are reviewed and approved by the appropriate personnel.
Payment scheduling: Once an invoice has been approved, Nanonets can schedule the payment, ensuring you meet your payment deadlines and maintain good vendor relationships.
Integrates with other tools: Nanonets integrates with Gmail, Google Drive, SharePoint, and Dropbox for easy document uploading and management. It also integrates with accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, Sage, and Zoho Books for seamless data transfer and financial management. You can even set up Zapier integrations to connect with hundreds of other apps and automate your workflows.
Analytics and reporting: The software generates detailed reports providing insights into your invoice processing. These reports can help identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, enabling you to make data-driven decisions.
Scalability: Whether you're handling hundreds or thousands of invoices, Nanonets can scale to meet your needs. And as your business grows, the software can adapt to accommodate increased invoice volumes without compromising speed or accuracy.
Security: With Nanonets, you can rest assured that your data is safe. GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA compliant, the software ensures top-tier data protection and privacy. All transactions and data transfers are encrypted, providing an additional layer of security.
Cloud-based: As a cloud-based solution, Nanonets allows for flexible access from any location. Your team can manage invoices from multiple sites, improving collaboration and productivity.
Numerous export options: CSV, PDF, Excel, JSON – Nanonets supports multiple export formats, allowing you to share and utilize your invoice data efficiently. This flexibility ensures compatibility with various systems and software, making data management easier and more efficient.
Customize the workflow: Tailor the invoice management workflow to fit your specific needs. You can set up custom approval paths, automate certain tasks, or add specific steps as required. This level of customization enables you to create a system that works seamlessly with your existing processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Continuous improvement: The AI learns and improves over time, adapting to changes in invoice formats or procedures. This constant learning enables Nanonets to deliver more accurate results, streamline operations, and enhance efficiency.
Final thoughts
Managing vendor invoices is critical to maintaining healthy vendor relationships, ensuring financial accuracy, and optimizing operational efficiency.
With Nanonets, you can automate your invoice management process, reducing errors, speeding up approvals, and freeing up valuable time for your team to focus on other crucial tasks. Our advanced AI technology, user-friendly interface, and robust integrations make Nanonets an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes.
Want to see how Nanonets can enhance your invoice management process? Schedule a demo with us today.
FAQs
What is included in a vendor invoice?
A vendor invoice typically includes the vendor's name and contact information, invoice number, date of issue, a detailed list of goods or services provided, the quantity, the price per unit, total amount due, payment terms, and due date.
What is the difference between a sales invoice and a vendor invoice?
A sales invoice is issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the goods or services sold and the amount owed by the buyer. On the other hand, a vendor invoice is sent by a vendor or supplier to a company, outlining the products or services provided and the payment due from the company.
What is the process of vendor invoices?
The vendor invoice process involves receiving the vendor invoice, verifying the details against the purchase order and goods received note, approving the invoice for payment, and then scheduling the payment. The invoice is then archived for future reference and auditing.
Is a vendor bill an invoice?
Yes, a vendor bill is another term for a vendor invoice. Both terms refer to the document a vendor or supplier sends to a company detailing the goods or services provided and the payment due.
What is vendor invoice management?
Vendor invoice management involves receiving, verifying, approving, paying, and archiving vendor invoices. This process can be automated using software like Nanonets, which uses AI technology to streamline and improve the efficiency of vendor invoice management.
What is the process of vendor invoices?
The process of vendor invoice involves several steps. Firstly, the vendor sends the invoice detailing the goods or services provided. The recipient then verifies the invoice details against the original purchase order, and goods received note. If everything matches, the invoice is approved for payment. The payment is then scheduled according to the terms agreed upon. After payment, the invoice is archived for record-keeping and auditing purposes.
What are the benefits of vendor invoice management?
Vendor invoice management offers several benefits, including improved operational efficiency, reduced errors, faster invoice approval and payment process, and enhanced vendor relationships. It also allows for better financial accuracy, valuable insights through data analysis, and significant time savings.
What is a vendor's invoice?
A vendor's invoice is a document a supplier or vendor issued to a company. It details the goods or services provided, the quantity, the price per unit, the total amount due, and the payment terms. This invoice serves as a request for payment from the company for the goods or services received.
How do vendors send invoices?
Vendors typically send invoices in a variety of ways depending on the preferences of the company they are invoicing. This could be via email, postal mail, or an electronic billing system. Some companies also use invoice management software like Nanonets to streamline the process, allowing vendors to upload invoices directly into the system.





.png)

.png)

.png)

.png)